AUTHOR: HAZEL DSOUZA
DATE:20/12/2023
Introduction
India’s trade agreements drive its position in the global economy, enabling seamless import and export operations. However, payment processing—a critical element—ensures that financial transactions are smooth, secure, and compliant with regulations. Whether for small-scale exporters or large corporations, understanding payment systems is essential for effective Processing For Trade.
Understanding Payment Processing in Trade
What is Payment Processing?
Payment processing Agreements In India involves transferring funds between buyers and sellers in exchange for goods or services. It includes mechanisms to verify, authorize, and complete financial transactions Payment Processing For Trade securely.
Payment Methods in India for Trade Agreements
Traditional Payment Methods
- Cash Transactions: Though diminishing, they still exist in rural trade setups Payment Systems[1].
- Demand Drafts: Often used for bulk payments, ensuring safety and authenticity.
Modern Payment Methods
- Wire Transfers: Enable quick international payments through SWIFT.
- RTGS: Ideal for high-value, real-time settlements.
- UPI: Revolutionizing digital payments with its ease of use and widespread adoption.
Key Players in Payment Processing for Trade
Banking Institutions
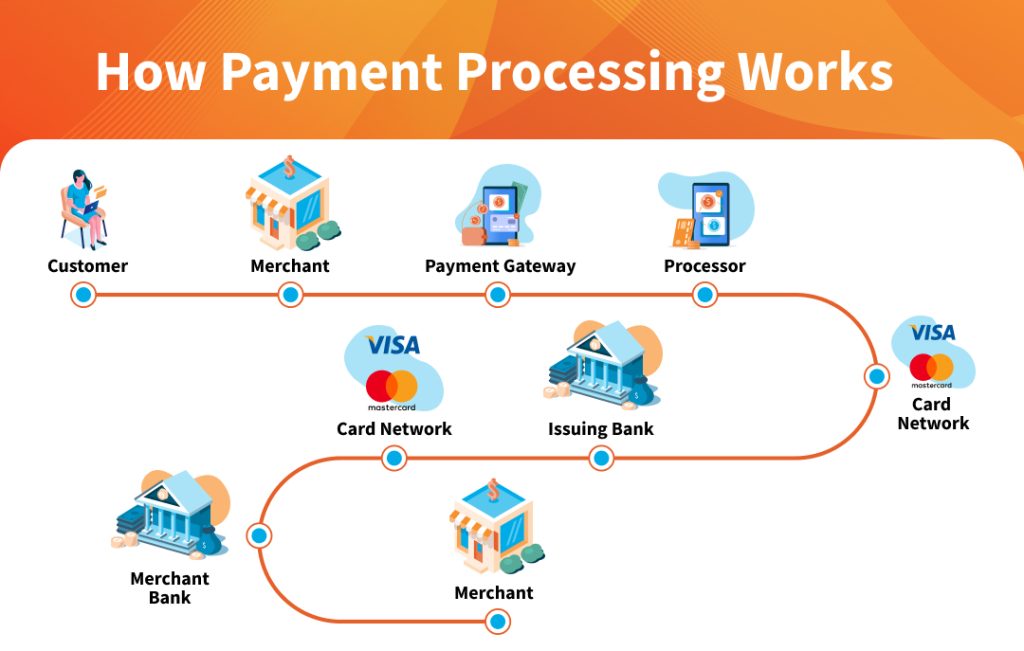
Trade in goods and services can serve as a substitute for trade in factors of production. Instead of importing a factor of production, International payment methods[2] a country can import goods that make intensive use of that factor of production and thus embody i Banks play a pivotal role in facilitating both domestic and international trade payments. They offer escrow services, credit lines, and forex management Payment Processing[3] Vital.
Payment Gateways
However, in practical terms, carrying out trade at an international level is typically a more complex process than domestic trade. Companies like Razor pay and Paytm enable quick digital payments[4], Trade Relationships[2] particularly for small and medium enterprises.
Role of RBI (Reserve Bank of India)
The RBI regulates trade payment systems, International trade[5] ensuring they comply with domestic and international standards, including FEMA guidelines Trade in goods and services can serve as a substitute for trade in factors of production. Instead of importing a factor of production, a country can import goods that make intensive use of that factor of production and thus embody .
Challenges in Payment Processing for Trade Agreements
Regulatory Hurdles
However, in practical terms, carrying out trade at an international level is typically a more complex process than domestic trade. Navigating complex regulations can slow down payment approvals, especially for international transactions. elatively minor factor of carbon emissions, albeit increased food localization may also enable additional, more significant
Currency Exchange Issues
quality standards or different levels of controllability by local production Fluctuating exchange rates often impact payment values, leading to losses or mismatches.
Technology Gaps in Rural Areas
in practical terms, carrying out trade at an international level is typically a more complex process than domestic trade. Limited digital infrastructure hampers payment processing in rural trade hubs However, in practical terms, carrying out trade at an international level is typically a more complex process than domestic trade..
Regulatory Framework in India
Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA)

Trade in goods and services can serve as a substitute for trade in factors of production. Instead of importing a factor of production, a country can import goods that make intensive use of that factor of production and thus embody FEMA governs foreign payments, ensuring smooth cross-border transactions while mitigating risks of money laundering.
Compliance Standards for Trade Payments
Trade payments must adhere to anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) norms, as mandated by Indian authorities in practical terms, carrying out trade at an international level is typically a more complex process than domestic trade. .
Innovations in Payment Processing
Blockchain in Trade Payments
Thus, international trade is mostly restricted to trade in goods and services, and only to a lesser extent to trade in capital, labor, Blockchain ensures transparency, reduces fraud, and facilitates faster cross-border payments.

Digital Currencies and Trade
Trade in goods and services can serve as a substitute for trade in factors of production. Instead of importing a factor of production, a country can import goods that make intensive use of that factor of production and thus embody it. India’s CBDC (Central Bank Digital Currency) could reshape how international trade payments are processed.
Importance of Secure Payment Processing
Risks of Fraud
Fraudulent transactions can lead to financial losses and strained trade relationships. Trade in goods and services can serve as a substitute for trade in factors of production. Instead of importing a factor of production, a country can import goods that make intensive use of that factor of production and thus embody it.
Data Privacy Concerns
Protecting sensitive payment information is vital in today’s digital age. quality standards or different levels of controllability by local production Qualitative differences between substitutive products of different production regions may exist due to different legal requirements
Solutions to Enhance Security
Adopting two-factor authentication, encryption, and regular audits are some ways to fortify payment systems. Thus, international trade is mostly restricted to trade in goods and services, and only to a lesser extent to trade in capital, labour,
Case Studies: Successful Payment Systems in Indian Trade
India’s adoption of UPI for small-scale trade payments and the success of SWIFT for global transactions highlight how robust payment systems drive trade efficiency.
Future Trends in Payment Processing for Trade
The future of payment processing in trade lies in fintech innovations, including AI-powered systems, blockchain integration, and enhanced digital platforms. These advancements promise faster, safer, and more efficient payment solutions.
Conclusion
Payment processing is the backbone of trade agreements in India, ensuring seamless transactions and fostering trust between parties. As technology and regulations evolve, businesses must stay updated to leverage modern payment solutions effectively.
FAQs
1. What are the most common payment methods for trade agreements in India?
Wire transfers, RTGS, and UPI are widely used for their speed and reliability.
2. How does RBI regulate payment processing for international trade?
The RBI sets guidelines under FEMA and ensures compliance with AML and KYC norms.
3. What are the challenges Indian exporters face with payment processing?
Exporters often encounter regulatory delays, currency fluctuations, and limited digital infrastructure.
4. Can blockchain technology revolutionize trade payments in India?
Yes, blockchain offers transparency, speed, and security, making it a game-changer for trade payments.
5. How can businesses ensure secure payment processing in trade agreements?
By adopting encryption, fraud detection tools, and adhering to regulatory standards.
Conclusion
the landscape of payment processing for trade agreements in India is evolving rapidly. Embracing digital advancements, overcoming challenges, and fostering collaboration will pave the way for a robust and efficient payment ecosystem.






