AUTHOR : Sook
DATE : 26/12/2023
Introduction
India’s financial landscape is rapidly evolving, with digital payments and structured debt recovery[1] becoming key pillars of this growth. Payment processors ensure smooth, secure, and efficient online transactions, while debt recovery systems ensure financial accountability. This article dives deep into these interconnected systems.
Payment Processor or Debt Recovery in India: An In-Depth Look
India’s financial ecosystem has witnessed rapid evolution, especially in the areas of payment processing and debt recovery. Both play a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s economy, ensuring that businesses thrive while also managing risks. This article expands on the concepts of payment processors and debt recovery in India, highlighting their importance, challenges, and how they complement each other in today’s financial landscape.
What is a Payment Processor?
A payment processor[2] is a crucial component in facilitating digital transactions. It acts as a bridge between the customer, merchant, and bank, guaranteeing smooth and successful payment processing.
Payment processors are responsible for the authorization, routing, and finalization of the transactions.
Types of Payment Processors
- Payment Gateways: These allow merchants to accept payments via credit/debit cards, digital wallets, and other online payment systems.
- Merchant Account Providers: These are financial entities or services that temporarily hold a merchant’s funds before transferring them to the merchant’s bank account.
- Third-Party Processors: These include companies like Paytm, Razorpay, and PayU, which facilitate payments between buyers and sellers without directly involving banks.
Popular Payment Processors in India
India’s digital payment[3] revolution is driven by key players such as Razorpay, Paytm, and PhonePe. These companies have made online transactions incredibly convenient, allowing businesses of all sizes to adopt cashless payments.
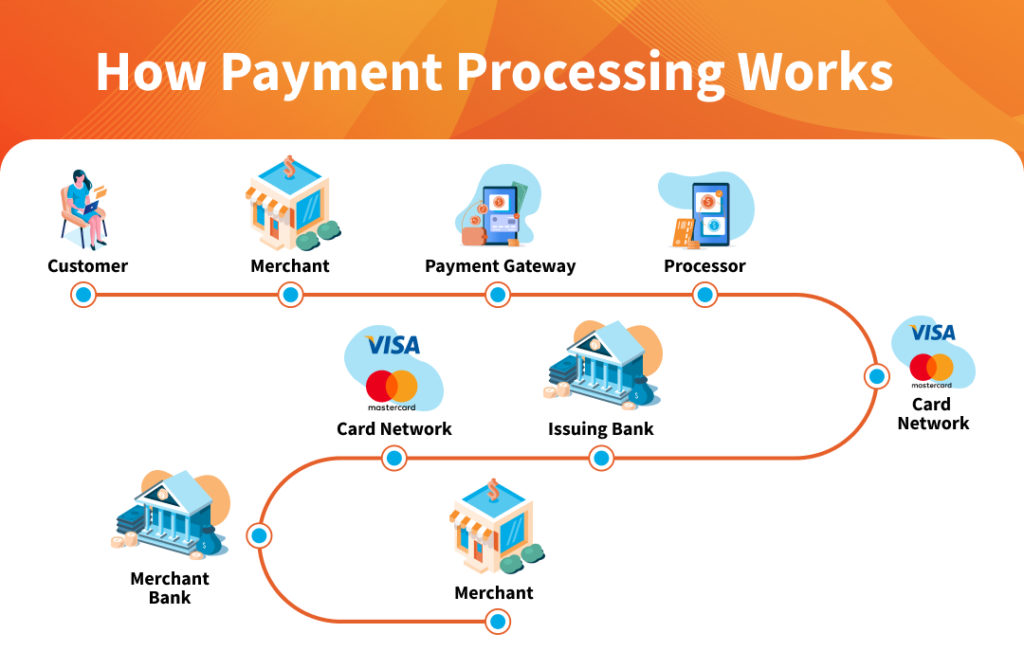
How Payment Processors Work
The mechanism behind payment processing is a multi-step procedure that involves several parties. When a customer chooses to buy online, the payment processor facilitates the transaction, ensuring it is completed safely and successfully
The Payment Processing Cycle
- Initiation: The process begins when a customer makes a payment via a payment gateway[4].
- Authorization: The payment processor verifies the customer’s information and confirms whether sufficient funds are available.
- Authentication: The system authenticates the payment using encryption and security measures.
- Settlement: Once confirmed, funds are transferred from the customer’s bank account to the merchant’s account.
Security Measures in Payment Processing
Payment processors take extra care to ensure that sensitive information such as credit card details and personal data are securely transmitted. To protect against fraud and cyber-attacks, they implement technologies such as:
- Encryption: Encrypting transaction data to prevent unauthorized access.
- Tokenization: Replacing sensitive data with randomly generated values (tokens).
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adding an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized access.
Challenges Faced by Payment Processors
Despite the convenience, payment processors face challenges such as:
- Fraudulent Transactions: A growing concern with increasing cyber-attacks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to government and industry regulations.
- Technical Glitches: Payment disruptions caused by server issues or system failures.
The Role of Payment Processors in India’s Digital Transformation
Payment processors have become the backbone of India’s push towards a cashless economy. Initiatives such as the Digital India campaign, along with government-backed platforms like UPI (Unified Payments Interface), have significantly changed how payments are made in India.
Driving Digital Payments
With a rise in smartphone usage and internet penetration, payment processors have simplified payments for both individuals and businesses. Today, payment processors handle millions of transactions per day, ranging from small micro-transactions to large e-commerce purchases.
Promoting Financial Inclusion
One of the most significant contributions of payment processors in India is their role in financial inclusion. By providing access to digital financial services, they are enabling millions of unbanked and underbanked individuals in rural areas to engage in financial activities, making them a crucial part of India’s financial inclusion strategy.
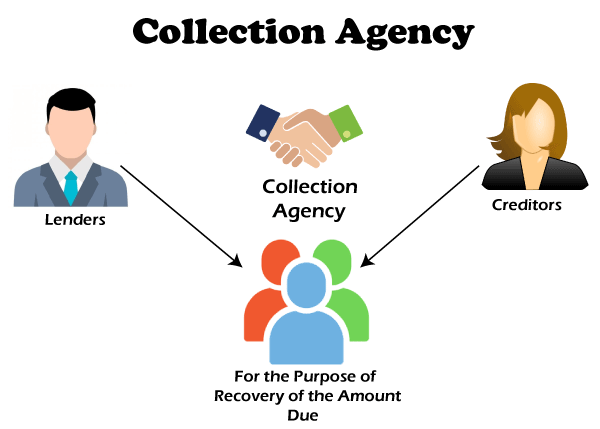
What is Debt Recovery?
Debt recovery refers to the process by which creditors collect payments from borrowers who have defaulted on their loans. Debt recovery is an essential part of the financial ecosystem as it ensures that businesses and banks receive the funds they are owed, which helps maintain the stability of the financial system.
Importance of Debt Recovery
Debt recovery ensures that lenders can continue to provide credit to borrowers. Without efficient debt recovery systems, businesses may experience liquidity issues, which can hinder their operations. It also helps in managing non-performing assets (NPAs), which are a significant concern for Indian banks.
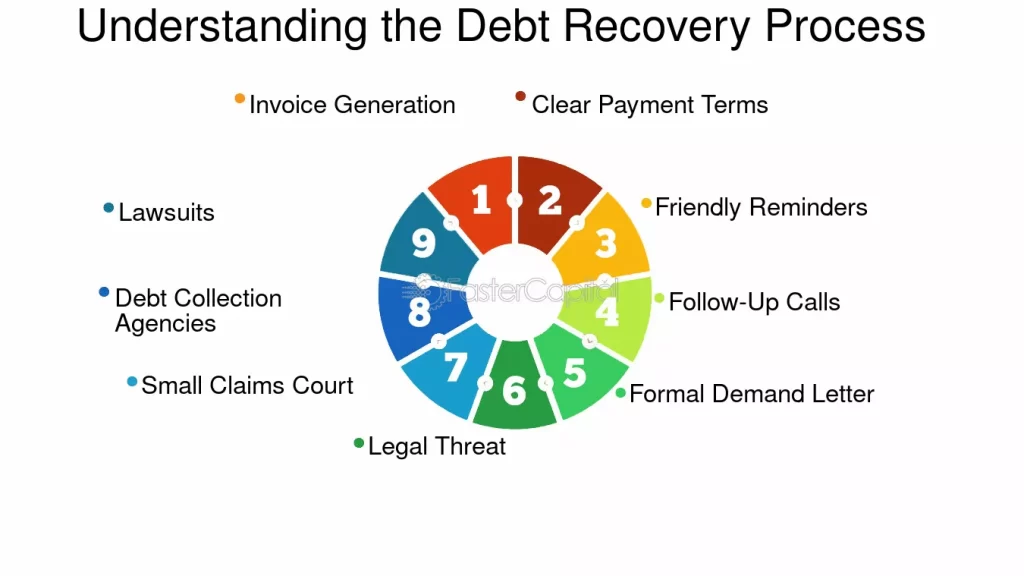
Debt Recovery Mechanisms in India
Debt recovery in India is governed by a combination of legal and financial mechanisms. The country has seen significant reforms in this area, with the introduction of specialized laws and frameworks aimed at improving the recovery process.
Legal Frameworks for Debt Recovery
- SARFAESI Act: The Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act empowers banks and financial institutions to take action against borrowers who default on secured loans.
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC): This comprehensive law provides a structured process for resolving insolvency issues and recovering debts from defaulting companies.
- Debt Recovery Tribunals (DRTs): These are specialized courts set up for expediting the recovery of debts by financial institutions.
Methods of Debt Recovery
- Negotiation: Often the first step, where creditors attempt to reach a settlement with the debtor.
- Legal Action: When negotiation fails, creditors may resort to legal measures, including filing suits in court or approaching Debt Recovery Tribunals.
- Seizure of Assets: As a last resort, assets can be auctioned or liquidated to recover the owed amount.

Challenges in Debt Recovery
Debt recovery is not without its challenges. Both businesses and banks often face hurdles in ensuring that debts are recovered on time.
Delayed Payments
Delayed payments can create liquidity issues, affecting cash flow and impacting business operations.
Legal Hurdles
Debt recovery through legal channels can be a time-consuming and complex process. Cases often take years to resolve, which leads to delays in receiving payments.
Ethical Considerations
While recovering debts is important, it is equally necessary to ensure that ethical practices are followed during the recovery process. Harassment or unfair treatment of borrowers can lead to legal complications.
Payment Processors and Debt Recovery: Complementary Roles
Although payment processors and debt recovery processes serve different purposes, they are closely related. Payment processors ensure smooth and efficient transactions, while debt recovery focuses on ensuring that overdue debts are paid. Together, they form a cohesive system that maintains financial stability[5].
Key Differences
- Payment Processors focus on managing transactions at the point of sale or online payment stage.
- Debt Recovery comes into play when customers fail to pay their dues, and creditors need to take action to recover the funds.
How They Work Together
Payment processors enable businesses to collect payments efficiently and securely, reducing the likelihood of defaults. Meanwhile, debt recovery ensures that even when defaults happen, there are mechanisms in place to recover the owed amounts, keeping businesses financially stable.
Future of Payment Processing and Debt Recovery in India
As technology continues to evolve, the future of both payment processing and debt recovery looks promising.
Emerging Technologies
- Blockchain: Ensuring more secure and transparent payment transactions.
- AI and Automation: These technologies will revolutionize debt recovery by improving efficiency and reducing human error.
Evolving Debt Recovery Practices
In the future, businesses and financial institutions will likely integrate artificial intelligence and data analytics to predict payment behavior and take proactive debt recovery steps.
Conclusion
In the context of India’s growing digital economy, both payment processors and debt recovery systems play crucial roles in ensuring financial stability. By embracing technology and regulatory reforms, both sectors are set to evolve, driving greater financial inclusion and empowering businesses to thrive in the digital age.
FAQs
1. How do payment processors secure transactions?
Payment processors use encryption, tokenization, and multi-factor authentication to ensure the security of transactions.
2. What is the role of Debt Recovery Tribunals (DRTs)?
DRTs are specialized courts that handle cases related to debt recovery, expediting the process for financial institutions.
3. Can payment processors help reduce debt recovery issues?
Yes, by ensuring timely payments and preventing fraud, payment processors can reduce the need for debt recovery.
4. What are the main challenges in debt recovery in India?
Challenges include delayed payments, legal hurdles, and ethical concerns during the recovery process.
5. How is technology changing payment processing in India?
Technologies like AI, blockchain, and machine learning are enhancing the security, efficiency, and transparency of payment transactions.