AUTHOR:HAZEL DSOUZA
DATE:26/12/2023
Outstanding debt among high-risk Payment Service Providers (PSPs) in India has become a pressing concern in the country’s financial landscape. As the financial sector evolves and embraces digital transactions, the challenges posed by outstanding debt from high-risk PSPs cannot be ignored.
Introduction
Definition of High-risk PSP Outstanding Debt
High-risk PSP outstanding debt refers to the accumulated financial obligations of payment service providers deemed to carry higher risks, often associated with factors like inadequate risk management, technological vulnerabilities, and regulatory non-compliance.
Significance in the Indian Financial Landscape
The growing prevalence of digital transactions makes understanding and addressing outstanding debt crucial for maintaining the integrity and stability of the Indian financial system Payment[1] Service Providers play a vital role in facilitating financial transactions between consumers and businesses, acting as intermediaries in the payment process.

Role in Financial Transactions
PSPs enable the seamless transfer[2] of funds, contributing to the efficiency and convenience of modern financial transactions. Various factors contribute to the accumulation of outstanding debt among PSPs, including inadequate risk management practices, High risk PSP Outstanding debt in India increased market competition, and technological challenges leading to fraud risks.
High-risk PSPs in India
Regulatory bodies and financial institutions must identify and classify payment service providers with heightened risk profiles. Examining the regulatory framework and oversight mechanisms in place to monitor and control the activities of high-risk PSPs. Outstanding Invoice[3] The presence of high-risk PSPs poses potential threats to the stability and reputation of the financial sector in India.
Factors Leading to Outstanding Debt
Lack of Risk Management Strategies
High-Risk Payment Processing[ often struggle with inadequate risk management strategies, leading to the accumulation of outstanding debt. The competitive nature of the industry[4] and rapid market dynamics contribute to the challenges faced y PSPs in managing outstanding debt.
Technological Challenges and Fraud Risks
The reliance on technology exposes PSPs to potential vulnerabilities, including fraud risks, leading to the accumulation of outstanding Debt collection[5] specific cases of high-risk PSPs in India and the repercussions faced by the financial ecosystem. Drawing lessons from past incidents to strengthen risk management and regulatory measures within the payment industry.
The Burden on Financial Institutions
How Outstanding Debt Affects Banks and Financial Institutions
Exploring the ripple effects of outstanding debt on traditional financial institutions and banks. Highlighting strategies that financial institutions can employ to mitigate the risks associated with outstanding debt.
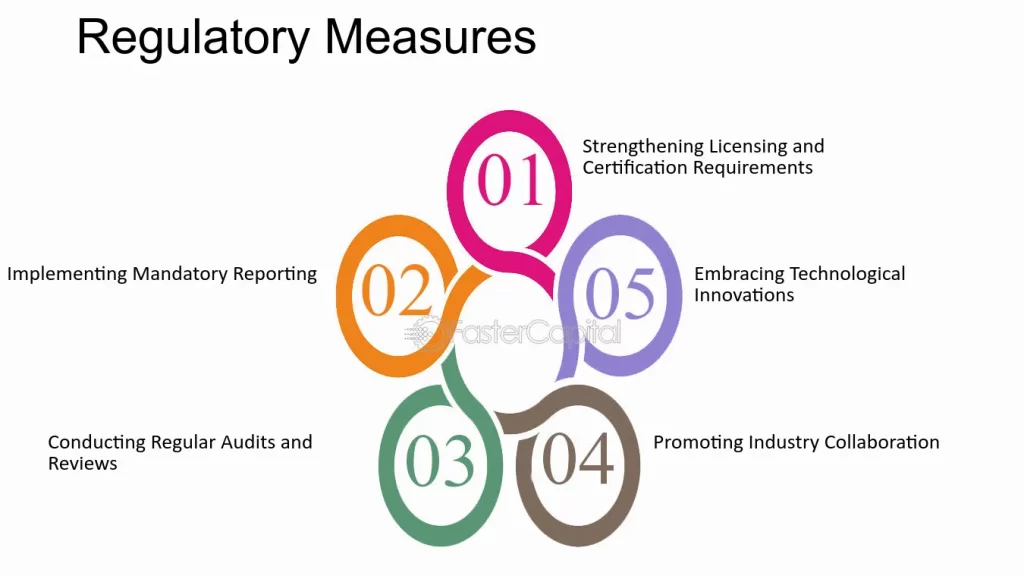
Regulatory Measure
Steps Taken by Regulators to Address Outstanding Debt
Analysing the regulatory actions taken to address outstanding debt and enhance the resilience of the payment industry. Predicting future regulatory developments and their potential impact on high-risk PSPs in India.
Impact on Consumers
Consumer Risks Associated with High-risk PSPs
Discussing the risks that consumers face when engaging with high-risk PSPs and ways to safeguard their financial interests. Providing practical steps consumers can take to protect themselves from potential risks associated with high-risk PSPs. Advocating for collaborative efforts among regulatory bodies, financial institutions, and PSPs to address outstanding debt collectively.
Initiatives to Address Outstanding Debt Collectively
Exploring initiatives and programs aimed at fostering collaboration and improving the overall health of the payment industry. Highlighting technological innovations that can assist in mitigating outstanding debt risks among PSPs. Exploring the role of advanced analytics and artificial intelligence in enhancing risk management within the payment industry.

The Way Forward
Recommendations for a Sustainable and Secure Payment Ecosystem
Providing recommendations for creating a sustainable and secure payment ecosystem in India. Discussing anticipated trends and developments in the payment industry that can shape the future landscape.
Conclusion
addressing high-risk PSP outstanding debt is essential for fostering a secure and resilient payment ecosystem in India. Through collaboration, regulatory measures, and technological advancements, the industry can navigate challenges and embrace a sustainable future.
FAQs
- How can consumers identify high-risk PSPs?
- Look for regulatory certifications and compliance.
- Research and read reviews from other users.
- What steps are regulators taking to address outstanding debt?
- Implementing stricter oversight and compliance measures.
- Collaborating with industry stakeholders to enhance regulations.
- Are there any technological solutions to mitigate outstanding debt risks?
- Yes, advancements in analytics and AI offer promising solutions.
- Implementing secure and robust technology infrastructure is crucial.
- How can financial institutions collaborate to manage outstanding debt?
- Establishing communication channels for sharing insights and best practices.
- Joining hands in collective efforts to tackle shared challenges within the industry.
- What role do consumers play in mitigating risks associated with high-risk PSPs?
- Staying informed about the latest developments in the payment industry.
- Reporting any suspicious activities or transactions promptly.