AUTHOR : RIVA BLACKLEY
Introduction
India’s cultural heritage is a mosaic of diverse civilizations, each leaving behind a unique footprint in the form of artifacts However, many of these artworks are now facing the threat of extinction due to various factors. This article aims to shed light on the issue of high-risk PSP rare artifacts in India.
Understanding High-Risk PSP
High-risk PSP refers to the heightened need for preservation, security, and protection of artifacts that face an increased risk of being lost or damaged. These artifacts include ancient manuscripts, sculptures, paintings, and other culturally significant items.
Historical Context of Rare Artifacts in India
India’s history is a tapestry woven with threads of art, architecture, and craftsmanship. From the Indus Valley Civilization to the Mughal era, every period has contributed to the rich tapestry of rare artifacts. However, the passage of time, coupled with environmental factors, poses a threat to their existence.
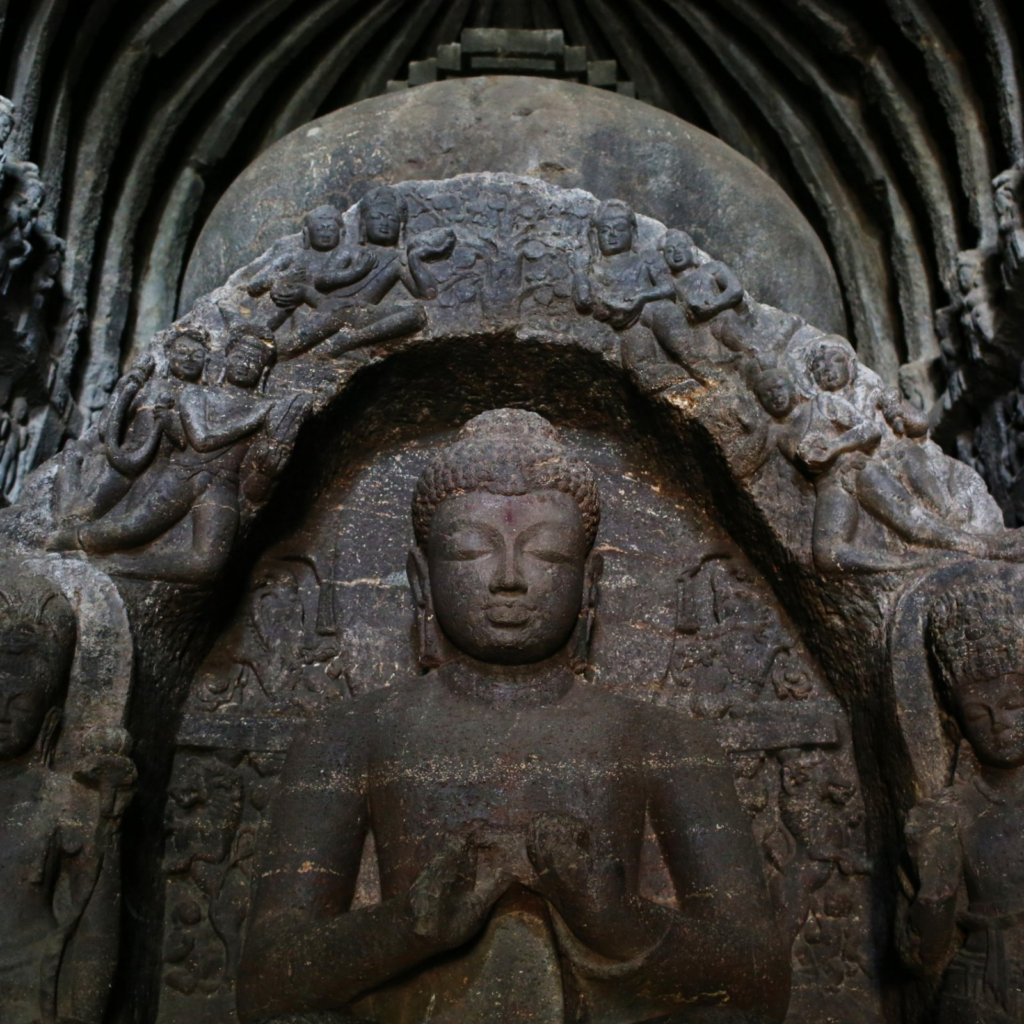

Challenges Faced by Rare Artifacts in India
The challenges are multi-faceted, ranging from illegal trade and environmental decay to the lack of awareness about the importance of preservation. Legal trafficking of artifacts remains a significant concern, leading to the loss of invaluable cultural heritage.
Efforts in Protecting Rare Artifacts
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the Indian government[1] has implemented various initiatives and policies to protect rare artifacts. Non-governmental organizations also play a crucial role in the conservation efforts, working hand in hand with authorities.
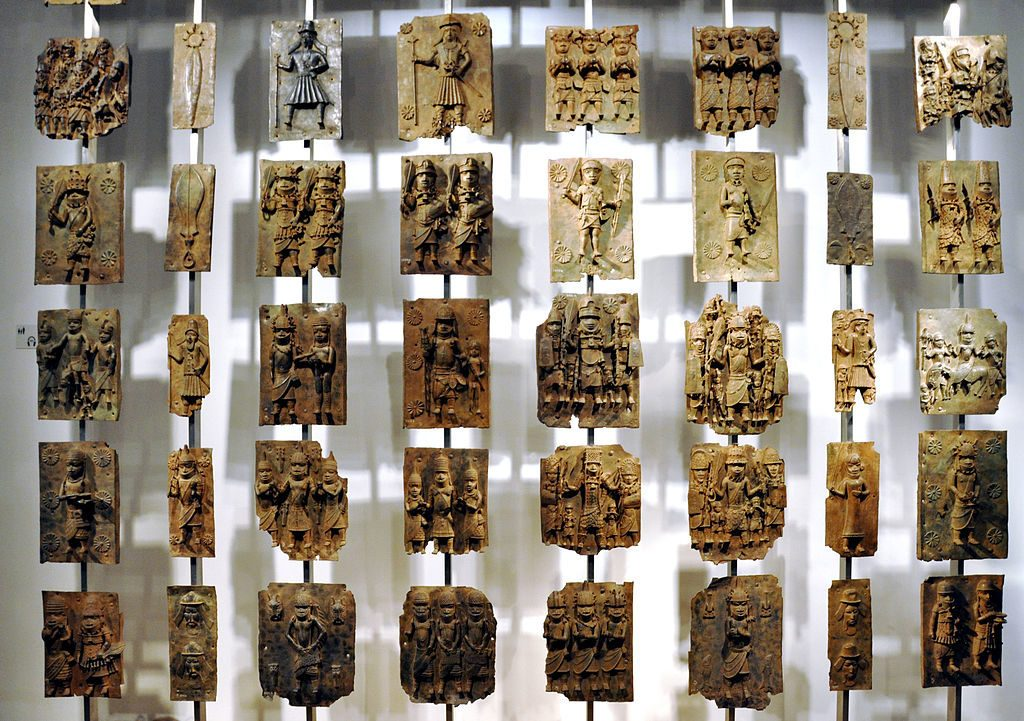

Noteworthy High-Risk PSP Rare Artifacts
Among the myriad of rare artifacts, some stand out as particularly vulnerable. The intricately carved sculptures of Khajuraho and the ancient manuscript s of Nalanda are examples of artifacts facing a high risk[2].
Legal Frameworks for Artifact Protection
To combat illegal trade and also ensure the protection of rare artifacts, India has stringent laws and regulations in place. Offenders face severe consequences, including hefty fines and imprisonment.
The Role of Technology in Preservation
Modern technology has become an ally in the battle for preservation. Advanced imaging techniques, climate-controlled storage, and also 3D printing contribute to the safeguarding of artifacts.
Community Involvement in Artifact Protection
Community awareness is pivotal in high-risk customer[3] ensuring the long-term preservation of rare artifacts. Successful case studies demonstrate the positive impact of involving local communities in conservation efforts.
International Collaboration
Recognizing the global significance of cultural heritage, India actively collaborates with international bodies and other nations to protect rare artifacts[4] These collaborations facilitate the exchange of knowledge and resources.
Educational Programs on Artifact Preservation
Educating the public about the importance of artifact preservation is a cornerstone of conservation efforts. Ongoing programs aim to raise awareness and foster a sense of responsibility among the populace.
Future Prospects for Rare Artifact Conservation
As technology advances, so do the prospects for artifact conservation. Emerging technologies coupled with sustainable practices offer hope for the continued preservation of India’s rare artifacts.
The Threat to India’s Cultural Heritage
Illegal trade remains a major menace, with priceless artifacts being smuggled out of the country, often ending up in private collections or on the black market. Additionally, environmental factors such as pollution, climate change, and natural disasters pose significant threats to the longevity of these artifacts.
Innovative Preservation Techniques
In the quest to combat these challenges, India has embraced innovative preservation techniques. Cutting-edge technologies like 3D scanning and virtual reality are being employed to create digital replicas of artifacts, ensuring their accessibility even in the face of physical deterioration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the urgency to protect high-risk payment[5] PSP rare artifacts in India cannot be overstated. While challenges persist, concerted efforts from the government, NGOs, and the public can ensure the survival of these cultural treasures for generations to come.
FAQS
- How can individuals contribute to the protection of rare artifacts?
- Individuals can contribute by staying informed, reporting illegal activities, and supporting local conservation initiatives.
- Are there specific regions in India more prone to artifact loss?
- Yes, regions with high tourism, poor security, and also environmental challenges are more susceptible.
- What legal consequences exist for those involved in illegal artifact trade?
- Offenders may face heavy fines, imprisonment, and the confiscation of artifacts.
- How can technology aid in artifact preservation?
- Technology aids preservation through advanced imaging, climate control, and also 3D printing for replication.
- What is the role of international collaboration in artifact conservation?
- International collaboration facilitates knowledge exchange, resource sharing, and a collective approach to protecting cultural heritage.




